How a focus on accurate data and on Native communities helped end prison gerrymandering in Washington State.
by Aleks Kajstura,
December 2, 2019
Prison Policy Initiative Legal Director Aleks Kajstura sat down with Heather Villanueva, Deputy Director of More Equitable Democracy to discuss their recent win in Washington that made that state the 5th to end the practice of giving extra political representation to the legislative districts that host prisons. (Shortly after Washington’s bill became law, Nevada became the 6th state to pass this legislation.)
- Aleks:
-
Can you tell us a little about More Equitable Democracy and how fixing the Census Bureau’s prison miscount fit into its mission?
- Heather:
-
More Equitable Democracy is a nonprofit advocacy organization working at the intersection of racial justice and democracy reform. One of the things we are concerned about is the basic building blocks of redistricting: the Census. Right now the census is coming up and facing quite a few serious financial and logistical challenges. A compromised Census will have serious implications for communities of color and for fair political representation. One of our priorities is to bridge our traditional push for full participation in the census count with larger policy goals of redistricting and redistricting reform.
For More Equitable Democracy, we tend to take a bigger view than just redistricting reform because we want to see bigger changes than just who draws the lines. It’s really about how the whole system of elections is created to either lift up some voices or to silence and put significant barriers in front of others. We’re really interested in developing new ways to build strong coalitions of reformers — and people of color in particular — to really transform our democracy.
- Aleks:
-
You are a new organization working in a number of states on a number of issues and the Washington bill to end prison gerrymandering was one of your first victories. How did you pick this bill to work on?
- Heather:
-
More Equitable Democracy seeks to make structural improvements to democracy and we identified Washington as one of a handful of states where we think we can make the biggest impact. As we considered what issues to prioritize in Washington, we knew that prison gerrymandering reform was gaining traction nationally, but had not been pursued in Washington. So when we saw legislative interest in ending prison gerrymandering, we knew it was an important issue and one that would be a great fit for our other democracy reform efforts in the state, including ranked choice voting, and securing $15 million for community-based census outreach to support an accurate count.
- Aleks:
-
In the past, we’ve talked about how Washington has fewer clusters or large prisons than states like New York and Maryland where the vote dilutive impact of prison gerrymandering is quite stark. Can you tell me why you thought it important to focus on prison gerrymandering even in states like Washington where the numerical impact is not as extreme?
- Heather:
-
That’s right, judging by the numbers, the prison gerrymandering problem in Washington State could be viewed as relatively minor. But the state draws its districts with far greater population equality than most, so Washington was a good place to focus on improving the accuracy of the redistricting data. As you know, what is important about the Census and redistricting is not just that everyone is counted, but where they are counted.
Beyond the simple calculations of vote dilution, we thought it was important to highlight the unique harms on Native American communities. I’m glad that we could help provide a platform for voices from these often overlooked communities, and I thought that the testimony of Patricia Whitefoot of the Yakama Nation was particularly effective raising the harm caused by counting their disproportionately incarcerated members in western Washington prisons rather than in their homes on the Yakama Reservation and discussing how this overlapped with other harmful redistricting decisions.
- Aleks:
-
Ending prison gerrymandering is the rare kind of reform that can benefit almost everyone in the state in one way or another. About the only people who have nothing to gain from reform are the people who live immediately adjacent to the state’s largest prison. Sometimes, though, reform efforts get hijacked by the false myth that changing electoral data will impact funding received by rural communities, and the effort stalls when faced with so much false urban vs rural tension. I’m really impressed that Washington (and Nevada) managed to pass this legislation in just one session, whereas other states have struggled for years. What do you think that folks in other states should see as keys to your success?
- Heather:
-
I think getting the bill passed was a combination of making the right choices at the start and then a lot of hard work.
It probably helped us that legislators were fairly new to the issue of prison gerrymandering, so we were able to keep ahead of any misinformation before it became entrenched.
We also used some messaging that was pretty different than that used in New York and Maryland and in other states. Rather than talk about stopping “gerrymandering” we focused on improving the accuracy of the data. In fact “ensuring accurate redistricting” became the bill’s tagline.
Focusing on data accuracy made a lot of sense in Washington State because we didn’t have the New York-style big numerical impact of prison gerrymandering with the obvious inequality and immediate impact on outcomes. In addition, focusing on “accurate redistricting” allowed us to avoid the political squabbling that “gerrymandering” conversations often illicit and instead start and end with something that everyone agrees on: the idea that the underlying data should be accurate.
This accuracy framework was also a natural fit with our organizational quest for structural reforms for a better democracy. As an organization, More Equitable Democracy does not just focus on what happens when the maps are drawn, we look at the entire process from the bottom up.
- Aleks:
-
That’s a good point. I know you chose that strategy because you thought it was best for the state of Washington, but this accuracy framing will be really important for the Census Bureau to hear when they review the issue again for the 2030 Census. And speaking of the Census Bureau, that now six states have chosen to fix this flaw in the Census, it really increases the pressure on the Bureau to provide a national solution.
Nevada moved swiftly, ending prison gerrymandering in a single legislative session.
May 31, 2019
For immediate release — Yesterday, Nevada Governor Steve Sisolak signed a bill into law ensuring that people in state prisons will be counted as residents of their home addresses when new legislative districts are drawn. The new law makes Nevada the sixth state to end the practice known as prison gerrymandering, after Washington passed its own law just last week.
The Nevada Constitution states that, for the purposes of voting, people in prison should be counted as residents of their hometowns. However, the Census Bureau counts incarcerated people as residents of the places where they are incarcerated. As a result, when Nevada used Census counts to draw past legislative districts, it unintentionally enhanced the weight of votes cast in districts containing prisons — at the expense of all other districts in the state.
“Nevada’s new law recognizes that ending prison gerrymandering is an important issue of fairness,” said Aleks Kajstura, Legal Director of the Prison Policy Initiative. “All districts — some far more than others — send people to prison, but only some districts contain prisons. Counting incarcerated people as residents of the prison gives extra representation to the prison district, dilutes the votes of everyone who does not live next to the state’s largest prison, and distorts the constitutional principle of one person, one vote. This new law offers Nevada voters a fairer data set on which future districts will be drawn.”
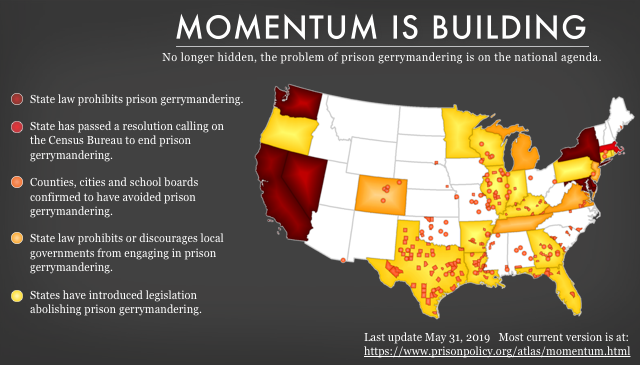
The legislation, passed as AB 450, applies only to redistricting and will not affect federal or state funding distributions.
Six other states have legislation to end prison gerrymandering pending in the current session. “We applaud Washington and Nevada for enacting common-sense solutions in a single legislative session,” Kajstura said. “Other states currently considering similar bills should follow its example.”
Washington State moved swiftly, ending prison gerrymandering in a single legislative session.
May 21, 2019
For immediate release — Today, Washington State Governor Jay Inslee signed a bill into law ensuring that people in state prisons will be counted as residents of their home addresses when new legislative districts are drawn, making Washington the fifth state to end the practice known as prison gerrymandering.
The Washington State Constitution states that, for the purposes of voting, people in prison should be counted as residents of their hometowns. However, the Census Bureau counts incarcerated people as residents of the places where they are incarcerated. As a result, when Washington State used Census counts to draw past legislative districts, it unintentionally enhanced the weight of votes cast in districts containing prisons — at the expense of all other districts in the state.
“Washington State’s new law recognizes that ending prison gerrymandering is an important issue of fairness,” said Aleks Kajstura, Legal Director of the Prison Policy Initiative, who was present when the bill was signed. “All districts — some far more than others — send people to prison, but only some districts contain prisons. Counting incarcerated people as residents of the prison gives extra representation to the prison district, dilutes the votes of everyone who does not live next to the state’s largest prison, and distorts the constitutional principle of one person, one vote. This new law offers Washington voters a fairer data set on which future districts will be drawn.”
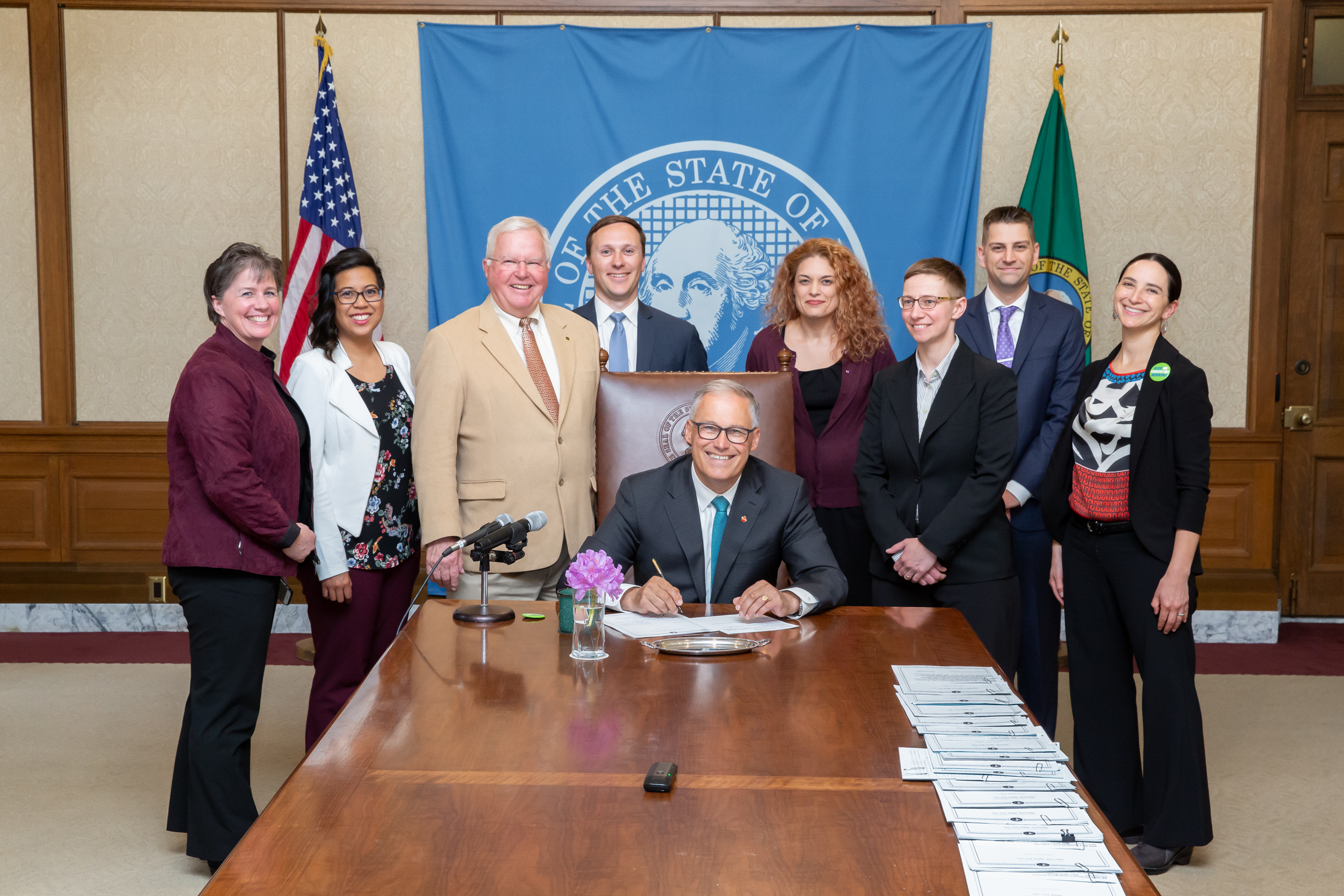

The legislation, passed as SB 5287, applies only to redistricting and will not affect federal or state funding distributions.
Five other states have legislation to end prison gerrymandering pending in the current session. “We applaud Washington State for enacting this common-sense solution in a single legislative session,” Kajstura said. “Other states currently considering similar bills should follow its example.”
The states with pending legislation include:
- Connecticut: HB 5611, introduced by the Government Administration and Elections Committee for the January Session, 2019.
- New Jersey: S758, “requir[ing] incarcerated individual from State to be counted at residential address for legislative redistricting purposes”, introduced by Senators Sandra Cunningham and Nilsa Cruz-Perez, January 9, 2018, and A1987, introduced by Assemblymembers Sumter, Mukherji, Quijano, and Pinkin, January 9, 2018.
- Oregon: HB 2492, “Relating to redistricting”, has chief sponsors Representative Holvey and Senator Prozanski and regular sponsors Representatives Nosse, Piluso, Sanchez, filed on January 14, 2019.
- Rhode Island: H 5513, “Residence of Those in Government Custody Act”, introduced by Representatives Williams, Vella-Wilkinson, Craven, Caldwell, and Almeida, February 14, 2019. And S 232, “Residence of Those in Government Custody Act”, introduced by Senators Metts, Nesselbush, Quezada, Cano, and Crowley, January 31, 2019.
- Texas: “An Act Relating to the inclusion of an incarcerated person in the population data used for redistricting according to the person’s last residence before incarceration” was filed by Representative Johnson as HB 104 on November 12, 2018.
Pending Governor Jay Inslee's signature, Washington State will become the fifth state to count incarcerated people at their home addresses during redistricting.
April 23, 2019
On April 23, the Washington state legislature passed a bill ensuring that incarcerated persons will be counted as residents of their home addresses when new legislative districts are drawn in Washington. The bill is now awaiting Governor Jay Inslee’s signature.
The Washington State Constitution states that, for the purposes of voting, people in prison should be counted as residents of their hometowns. However, the Census Bureau counts incarcerated people as residents of the places where they are incarcerated. As a result, when Washington State uses Census counts to draw legislative districts, it unintentionally enhances the weight of a vote cast in districts that contain prisons at the expense of all other districts in the state.
This problem is national, affecting not only Washington but all states. Our past research has found one state house district in Texas, for instance, that was 12% incarcerated people; and 15% of one Montana state house district consisted of incarcerated people imported from other parts of the state.
Washington State is poised to become the fifth state to correct this problem by adjusting Census data to count incarcerated persons at their home address, joining New York, Maryland, Delaware, and California. Nine other states have legislation pending in the current session.
The legislation, passed as SB 5287, applies only to redistricting and would not affect federal or state funding distributions.
“Washington’s legislation recognizes that prison-based gerrymandering is a problem of fairness,” said Aleks Kajstura, Legal Director of the Prison Policy Initiative. “All districts — some far more than others — send people to prison, but only some districts have large prisons. Counting incarcerated people as residents of the prison distorts the principle of one person, one vote. This new law offers Washington voters a fairer data set on which future districts will be drawn.”
The Washington State legislature is close to passing a bill enabling its redistricting commission to end prison gerrymandering.
by Aleks Kajstura,
April 16, 2019
Washington State is poised to become the fifth state to end prison gerrymandering. SB 5287, sponsored by Senators Darneille and Hunt, introduced on January 17, 2019; the bill passed the Senate on March 11, 2019, and the House on April 16, 2019.
Because the bill was amended in the House, it will now go back to the Senate for a concurrence vote. (The House amendment clarified how incarcerated people from out of state or with unknown addresses would be counted.)
The Census Bureau has decided to count incarcerated people in the wrong place again at the next Census, so states are taking action on their own now to avoid prison gerrymandering after the 2020 Census. Washington is one of ten states with bills to end prison gerrymandering pending this session, if the bills pass these states would join California, Delaware, Maryland and New York in ensuring equal representation for their residents.
If it passes, the bill would make New Jersey the fifth state to end prison gerrymandering.
by Aleks Kajstura,
February 26, 2019
The New Jersey State Senate passed a bill to end prison gerrymandering on Thursday, with bipartisan support. The identical Assembly counterpart to the bill, A1987, is still pending.
Our New Jersey campaign page has fact sheets, testimony, and other information on the effort to end prison gerrymandering in the state. We’re thrilled to see this bill moving forward after the last legislative session, where the legislation made it all the way to the Governor’s desk, only to be vetoed by former Governor Christie.
The Census Bureau has decided to count incarcerated people in the wrong place again at the next Census, so states need to take action on their own now to avoid prison gerrymandering after the 2020 Census. New Jersey is one of six states with bills to end prison gerrymandering pending this session, if the bills pass these states would join California, Delaware, Maryland and New York in ensuring equal representation for their residents.
Bills to end prison gerrymandering are pending in six states' new legislative sessions. Conn. prison gerrymandering challenge passes first hurdle in court.
by Aleks Kajstura,
February 21, 2019
On Tuesday, the NAACP’s lawsuit challenging prison gerrymandering in Connecticut survived the state’s motion to dismiss before the U.S. District Court for the District of Connecticut.
While the status quo is challenged in the courts, the state continues to consider a legislative solution. The Government Administration and Elections Committee heard testimony on House Bill 5611 last Friday. (Testimony from the hearing, and other info on efforts to end prison gerrymandering in Connecticut is available on our Connecticut campaign page.)
Connecticut is one of six states with bills to end prison gerrymandering pending this session:
- Connecticut:HB 5611, introduced by the Government Administration and Elections Committee for the January Session, 2019.
- New Jersey: S758, “requir[ing] incarcerated individual from State to be counted at residential address for legislative redistricting purposes”, introduced by Senators Sandra Cunningham and Nilsa Cruz-Perez, January 9, 2018, and A1987, introduced by Assemblymembers Sumter, Mukherji, Quijano, and Pinkin, January 9, 2018.
- Oregon: HB 2492, “Relating to redistricting”, has chief sponsors Representative Holvey and Senator Prozanski and regular sponsors Representatives Nosse, Piluso, Sanchez, filed on January 14, 2019.
- Rhode Island: H 5513, “Residence of Those in Government Custody Act”, introduced by Representatives Williams, Vella-Wilkinson, Craven, Caldwell, and Almeida, February 14, 2019. And S 232, “Residence of Those in Government Custody Act”, introduced by Senators Metts, Nesselbush, Quezada, Cano, and Crowley, January 31, 2019.
- Texas: “An Act Relating to the inclusion of an incarcerated person in the population data used for redistricting according to the person’s last residence before incarceration” was filed by Representative Johnson as HB 104 on November 12, 2018.
- Washington: “Ensuring accurate redistricting”, SB 5287, sponsored by Senators Darneille and Hunt, introduced on January 17, 2019.